Passive-aggressive behavior in children can manifest in various ways, making it crucial for parents and caregivers to recognize and address these tendencies early on. From subtle acts of defiance to veiled expressions of anger, examples of passive-aggressive behavior can be seen in daily interactions with kids. While dismissing such behavior as a phase or a harmless trait may be tempting, understanding the significance of addressing passive-aggressive behavior is paramount for fostering healthy emotional development in children. Let’s give you examples of passive-aggressive behavior in kids and how to help children navigate through these behaviors and cultivate more positive and assertive ways of dealing with their feelings.
Download and Start Your Free Trial of the Safes Parental Control App
What is Passive-Aggressive Behavior in Children?
Passive-aggressive behavior refers to a style of expressing anger, frustration, or resentment indirectly rather than directly addressing the issue at hand. This behavior can manifest in various ways, including procrastination, intentional inefficiency, sarcasm, backhanded compliments, and stubbornness.
The underlying causes of passive-aggressive behavior in children can be complex. It may stem from a fear of expressing negative emotions directly, a lack of assertiveness, or a learned behavior from observing passive-aggressive interactions in their environment. Additionally, children who have experienced trauma, have difficulty managing their emotions or have unresolved conflicts may be more prone to displaying passive-aggressive behavior.
Common triggers and situations that may elicit passive-aggressive behavior in children include feeling overlooked or dismissed, experiencing a perceived injustice, or being asked to do something they don’t want to do. These triggers often lead to a passive-aggressive response as a way to gain a sense of control or express their underlying anger or frustration indirectly.
The impact of passive-aggressive behavior on child development and relationships can be significant. It can hinder healthy emotional development, as children may struggle to communicate their feelings and needs effectively. This can lead to difficulties in establishing and maintaining positive relationships with peers, family members, and authority figures. Passive-aggressive behavior can also contribute to a negative and toxic environment, as it can create tension, misunderstandings, and resentment in relationships.
Passive-aggressive behavior can be a form of bullying. Passive-aggressive bullying involves using indirect tactics to manipulate or hurt others, often through subtle acts of defiance or backhanded remarks. This behavior can have a detrimental impact on the well-being and self-esteem of the individual being targeted.
Common Examples of Passive-Aggressive Behavior in Children
Let’s explore some examples of passive-aggressive behavior commonly seen in children.
Passive resistance and non-compliance: Children may exhibit passive-aggressive behavior through passive resistance and non-compliance, such as purposefully ignoring or procrastinating tasks assigned to them.
Sarcasm and backhanded compliments: Another example is the use of sarcasm and backhanded compliments, where children make seemingly positive remarks that carry a hidden negative message, often to express their dissatisfaction or annoyance.
Procrastination and intentional delays: Children may also engage in passive-aggressive behavior by intentionally procrastinating or causing delays when asked to complete certain tasks or responsibilities.
Silent treatment and withdrawal: The silent treatment and withdrawal involve children intentionally ignoring or avoiding communication with others to express their anger or frustration indirectly.
Indirect communication and manipulation: Passive-aggressive behavior can also be observed through indirect communication and manipulation, where children may use subtle tactics to convey their dissatisfaction or manipulate situations to their advantage.
“Forgetting” or “accidentally” neglecting responsibilities: Lastly, children may exhibit passive-aggressive behavior by conveniently “forgetting” or “accidentally” neglecting their responsibilities, thereby avoiding accountability.
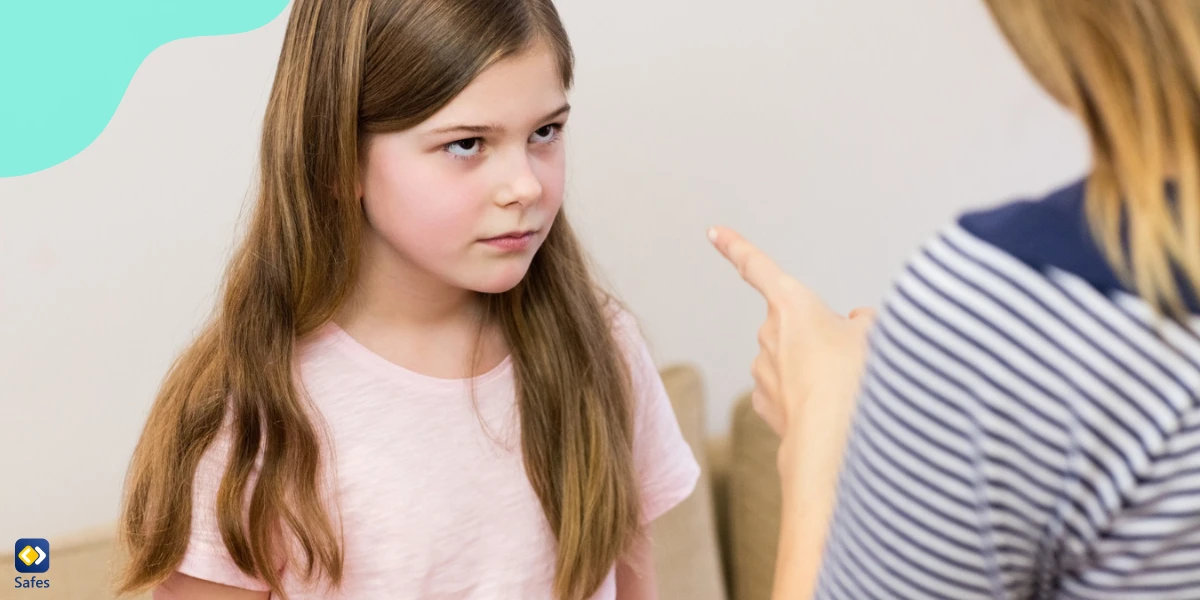

Impact of Passive-Aggressive Behavior on Parent-Child Relationship
Passive-aggressive behavior in children can have a significant impact on the parent-child relationship. It is characterized by indirect expressions of anger, frustration, or resistance, which can strain communication and lead to conflicts. The emotional toll on both parents and children is substantial, and if left unaddressed, passive-aggressive behavior can have long-term consequences. In the following, we will explore the issues related to the impact of passive-aggressive behavior in children on the parent-child relationship, focusing on strained communication and conflicts, the emotional toll on both parents and children, and the potential long-term consequences if these behaviors are not effectively addressed.
Strained communication and conflicts: Passive-aggressive behavior in children can create strained communication between parents and their child. Instead of openly expressing their feelings or concerns, children may resort to subtle acts of resistance, sarcasm, or silent treatment. This indirect communication style can make it challenging for parents to understand their child’s needs or address any underlying issues. Consequently, conflicts may arise, as parents struggle to navigate the hidden messages and frustration expressed through passive-aggressive behavior.
Emotional toll on both parents and children: The emotional toll of passive-aggressive behavior is not limited to the child alone but also affects parents. Constant exposure to passive-aggressive behavior can be emotionally draining and frustrating for parents, leading to feelings of helplessness, anger, or disappointment. Similarly, children engaging in passive-aggressive behavior may experience a range of emotions, such as resentment, anxiety, or confusion. This emotional turmoil can create a negative atmosphere within the parent-child relationship, impacting the overall well-being of both parties.
Long-term consequences if left unaddressed: If passive-aggressive behavior in children is not effectively addressed, it can have long-term implications for the parent-child relationship. The unresolved issues and strained communication can create a cycle of negative patterns that persist into adolescence and adulthood. Children who engage in passive-aggressive behavior may struggle with forming healthy relationships, expressing their emotions effectively, and resolving conflicts in a constructive manner. Additionally, the parent-child relationship may suffer from a lack of trust and open communication, hindering the development of a strong and nurturing bond.
Strategies for Addressing and Managing Passive-Aggressive Behavior
Addressing and managing passive-aggressive behavior in children is essential for promoting healthy communication and fostering strong parent-child relationships. By implementing effective strategies, you can help your child develop better ways of expressing their emotions and resolving conflicts. We will explore five strategies for addressing and managing passive-aggressive behavior: open and honest communication, setting clear expectations and boundaries, teaching assertiveness and problem-solving skills, providing positive reinforcement for healthy expressions of emotions, and seeking professional help if necessary.
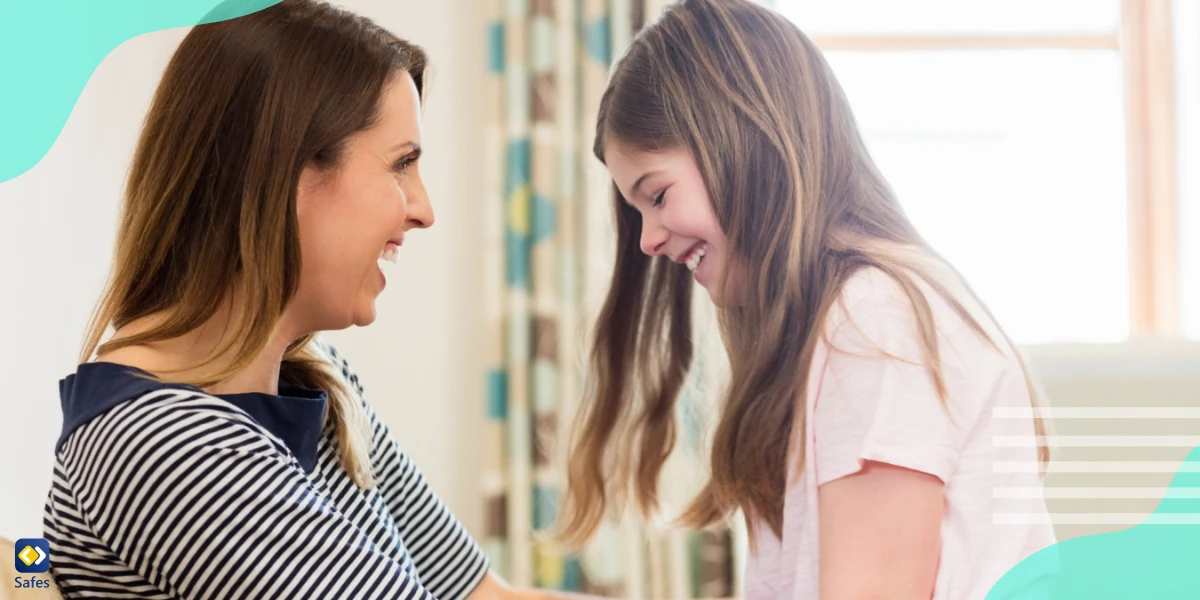

Open and Honest Communication with Your Child
Encouraging open and honest communication is crucial in addressing passive-aggressive behavior. Create a safe and non-judgmental environment where your child feels comfortable expressing their thoughts and emotions. Listen actively, validate their feelings, and encourage them to express themselves assertively. By fostering open communication, you can help your child understand the impact of their behavior and find healthier ways to address their concerns.
Setting Clear Expectations and Boundaries
As Signe Whitson explains in her article for Psychology Today, setting clear expectations and boundaries helps children understand what is acceptable behavior and what is not. Clearly communicate your expectations and establish consequences for passive-aggressive behavior. Consistently enforce these boundaries while also providing guidance on appropriate ways to express emotions. Setting clear rules and consequences provides structure and guidance for your child, helping them develop healthier communication habits.
Teaching Assertiveness and Problem-solving Skills
Teaching your child assertiveness and problem-solving skills empowers them to express their needs and concerns effectively. Encourage them to assertively communicate their feelings and expectations while also teaching them to actively listen and consider others’ perspectives. Teach problem-solving techniques, such as identifying issues, brainstorming solutions, and evaluating outcomes. Equipping your child with these skills empowers them to address conflicts directly and find positive resolutions.
Positive Reinforcement for Healthy Expressions of Emotions
Reinforcing healthy expressions of emotions helps your child understand the benefits of direct and honest communication. Praise and acknowledge their efforts when they express themselves assertively and address conflicts openly. Provide positive reinforcement by rewarding them with praise, encouragement, or small rewards for their positive behavior. This positive reinforcement motivates them to continue using healthy communication strategies.
Seeking Professional Help if Necessary
If passive-aggressive behavior persists or significantly impacts your child’s well-being, seeking professional help can be beneficial. A child psychologist or therapist can provide guidance and support in addressing and managing passive-aggressive behavior. They can help identify the underlying causes, develop personalized strategies, and offer tools for effective communication. Professional intervention can be invaluable in helping your child overcome passive-aggressive tendencies and build healthier relationships.
Utilizing Parental Control Apps as Support
Parental control apps can play an influential role in managing passive-aggressive behavior in kids by providing tools and features that promote healthy communication and responsible device usage. One such app that can be beneficial is the Safes parental control app.
The Safes app offers various features that can assist parents in addressing passive-aggressive behavior. Firstly, it allows you to set time limits and app restrictions, helping your kid develop a healthy balance between screen time and other activities. By setting boundaries, you can encourage open communication and reduce the likelihood of passive resistance or non-compliance.
Additionally, the Safes app enables you to monitor your child’s online activities, including social media usage. This feature helps you identify any indirect communication or manipulation tactics your child uses. By clearly understanding your child’s online behavior, you can effectively address any passive-aggressive tendencies.
Furthermore, the app allows you to block inappropriate web content, which can help prevent exposure to negative influences that may contribute to passive-aggressive behavior. By creating a safe online space, parents can encourage positive online interactions and reduce the chances of sarcasm or backhanded compliments.
The Safes parental control app can protect your child on all their smart devices on Android, iOS, Windows, and Mac platforms. Learn how to use Safes to put parental controls on different devices platforms using the following links:
- Windows parental controls
- Macbook parental controls
- Parental controls on Android
- iPhone parental controls
Start your 14-day free trial with Safes today to explore how it can support your efforts—no payment details required!
Please note that parental control apps should be complemented with open and honest communication, guidance, and support from parents or caregivers to address passive-aggressive behavior effectively.
Examples of Passive-Aggressive Behavior in Kids: Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing passive-aggressive behavior in children is crucial for their emotional development and effective communication skills. Examples of passive-aggressive behavior include passive resistance, sarcasm, procrastination, silent treatment, indirect communication, and manipulation. If left unaddressed, these behaviors can strain the parent-child relationship and have long-term consequences on the child’s well-being.
Strategies such as open communication, setting clear expectations, teaching assertiveness, and seeking professional help if necessary can help manage and address passive-aggressive behavior. Additionally, parental control apps like Safes can assist in creating a safe online environment and reducing exposure to negative influences. By addressing these behaviors early on, you can foster healthy emotional development and promote positive relationships with your child.
Your Child’s Online Safety Starts Here
Every parent today needs a solution to manage screen time and keep their child safe online.
Without the right tools, digital risks and excessive screen time can impact children's well-being. Safes helps parents set healthy boundaries, monitor activity, and protect kids from online dangers—all with an easy-to-use app.
Take control of your child’s digital world. Learn more about Safes or download the app to start your free trial today!